Wang Zifeng, a doctoral student in the team of Prof. Junguo Liu, recently developed a new method of remote sensing, to detect water body, Multispectral Water Index (hereinafter referred to as MuWI), which could effectively improve the resolution of the remote sensing water detection and reduces error from the low albedo and sun reflection phenomenon. Relevant papers have been published in a new issue of Remote Sensing journal.
The location and distribution of surface water bodies are key foundational information for many areas of concern, including hydrology and water resources, land use change, climate change impacts, coastal zone management, and the prevention and control of infectious diseases (such as malaria). Remote sensing can effectively provide the spatial distribution of surface water, which is the main way of water mapping.

Remote sensing water detection can identify surface water by capturing the reflection characteristics of water in different spectral bands. Based on this hypothesis, several mainstream remote sensing water detection methods such as NDWI, MNDWI, TCW and AWEI have been developed in recent decades. These methods were developed from Landsat series satellites and have been widely used in the above fields. However, the above methods still have shortcomings in spatial resolution, water identification accuracy, migration applicability and other aspects, which greatly limits the application of satellite remote sensing methods in urban water detection, runoff source area river network extraction and other high-resolution, high-precision scenarios.
Aiming at the problems in the water body remote sensing detection method, professor Junguo Liu’s team cooperated with the European space agency "sentry 2" satellite image data, creatively applied the machine learning SVM method, developed a new type of multispectral remote sensing water - MuWI detection method. This method can improve the water detection resolution from the traditional 30m or 20m to 10m, and significantly improve the traditional method in the low albedo pixel error (such as the typical building shadows, slope shadows, asphalt pavement).
Comparison of MuWI accuracy and application examples of new multi-spectral remote sensing water detection method
The new method, known as MuWI, also noticed the phenomenon of solar glint (commonly known as "shimmering") in land waters during remote sensing water detection for the first time. Previous studies of the phenomenon have generally focused on ocean remote sensing, radiometric atmospheric correction and computer vision. Due to the limitation of spatial resolution, the previous remote sensing water detection methods have not involved the solar reflux phenomenon, so some water detection omissions exist. Compared with the traditional method, the newly developed MuWI method optimizes the solar reflux phenomenon and can effectively suppress the leakage error caused by solar reflux.
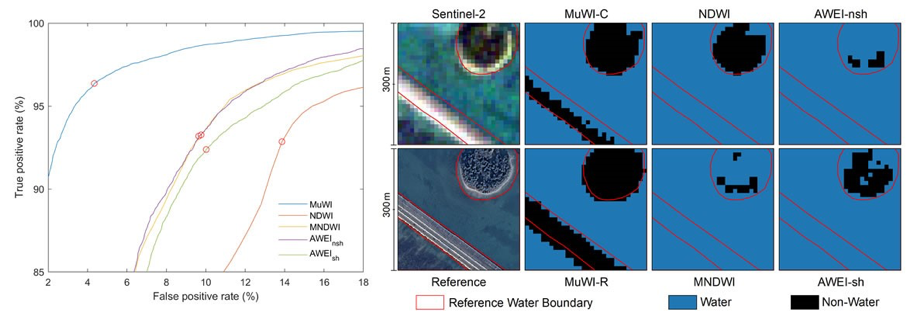
This method is expected to provide a new way for high precision water remote sensing mapping, land use mapping and related applications. The above research was supported by the strategic guidance special project of Chinese academy of sciences.
Link: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/10/10/1643